3.3 Instrument Design
HRC has been unavailable since January 2007. Information about the HRC is provided for archival purposes.
WFC is offered as shared risk in Cycle 33 and may receive minimal calibration. See the ACS website, Call for Proposals, and OPCR webpage for the latest status.
3.3.1 Detectors
The ACS channels feature the following detectors:
- The WFC employs a mosaic of two 4096 x 2048 Scientific Imaging Technologies (SITe) CCDs. The 15 × 15 µm2 pixels provide ~0.05 arcsec/pixel spatial resolution, with critical (Nyquist) sampling at 11,600 Å, resulting in a nominal 202 × 202 arcsec2 Field of View (FOV). The spectral sensitivity of the WFC ranges from ~3500 Å to ~11,000 Å, with a peak efficiency of 47% at ~6700 Å including the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA).
- The nonfunctioning HRC has a 1024 × 1024 SITe CCD, with 21 × 21 µm2 pixels that provided ~0.028 × 0.025 arcsec2/pixel spatial resolution with critical sampling at 6300 Å. This gave the HRC a nominal 29 × 26 arcsec2 FOV The spectral response of the HRC ranged from ~1700 Å to ~11,000 Å, and it had a peak efficiency of 27% at ~6400 Å including OTA.
- The SBC detector is a solar-blind CsI microchannel plate (MCP) with Multi-Anode Microchannel Array (MAMA) readout. It has 1024 × 1024 pixels, each 25 × 25 µm2 in size. This provides a spatial resolution of ~0.034 × 0.030 arcsec2/pixels, producing a nominal FOV of 34.6 × 30.5 arcsec2. The SBC UV spectral response ranges from ~1150 Å to ~1700 Å with a peak efficiency of 8.5% at 1260 Å.
The WFC & HRC CCDs
The ACS CCDs are thinned, backside-illuminated, full-frame devices. They are cooled by thermo-electric cooler (TEC) stacks housed in sealed, evacuated dewars with fused silica windows. The spectral response of the WFC CCDs is optimized for imaging at visible to near-IR wavelengths, while the HRC CCD spectral response was optimized specifically for near-UV wavelengths. The WFC CCD camera produces a time-integrated image in the ACCUM data-taking mode as did the HRC CCD before January 2007. As with all CCD detectors, there is noise and overhead associated with reading out the detector following an exposure.
The minimum WFC exposure time is 0.5 seconds. The minimum time between successive identical full-frame WFC exposures is 135 seconds. The dynamic range for a single exposure is ultimately limited by the depth of the CCD full well (~77,400 e– for the WFC and 155,000 e– for the HRC), which determines the total amount of charge that can accumulate in any one pixel during an exposure without physical saturation.
Cosmic rays will affect all CCD exposures. CCD observations should be broken into multiple exposures whenever possible to allow removal of cosmic rays in post-observation data processing (see Section 4.3.7).
The SBC MAMA
The SBC MAMA is a photon-counting detector that provides a two-dimensional ultraviolet imaging and spectroscopic capability. It is operated only in ACCUM mode. To protect the MAMA against permanent damage from over-illumination, local and global brightness limits of 50 counts/second/pixel and 200,000 counts/second, respectively, are imposed on all SBC targets and fields. Note that the linearity of the MAMA deviates by 1% at a local (pixel) count rate of ~22 counts/second/pixel, which is about half the bright object screening limit. The global count rate becomes similarly nonlinear at the screening limit of 200,000 counts/second. More information on the SBC's nonlinearity and bright object limits is given in Section 4.5, Section 4.6, and Section 7.2, and in ACS ISRs 1998-03, 1999-07, and 2019-10.
3.3.2 ACS Optical Design
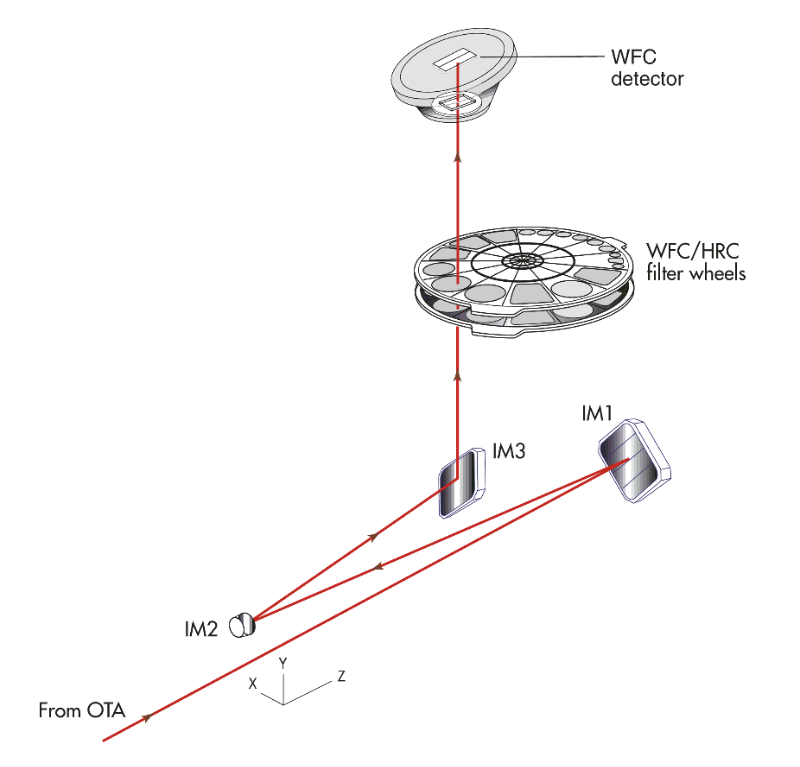
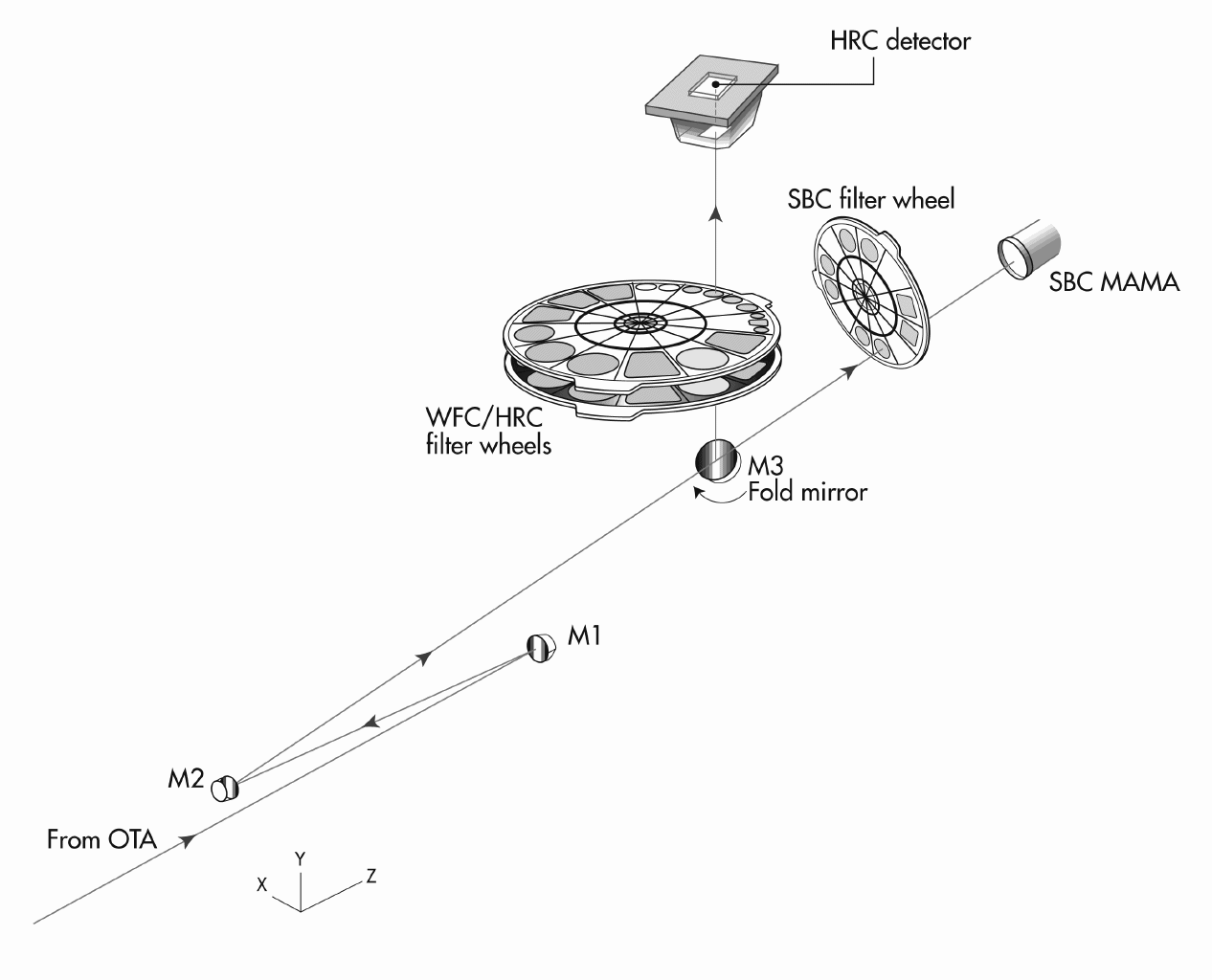
The ACS design incorporates two main optical channels: one for the WFC, and one which is shared by the HRC and SBC. Each channel has independent corrective optics to compensate for spherical aberration in the HST primary mirror. The WFC has silver-coated optics to optimize instrument throughput in the visible and near-IR. The silver coatings cut off wavelengths shortward of 3500 Å. The WFC has two filter wheels that it shared with the HRC, which offered the possibility of internal WFC/HRC parallel observing for some filter combinations when HRC was available. The optical design of the WFC is shown schematically in Figure 3.2. The HRC/SBC optical chain comprises three aluminized mirrors overcoated with MgF2, shown schematically in Figure 3.3. The HRC or SBC channels are selected by means of a plane fold mirror (M3 in Figure 3.3). The HRC was selected by inserting the fold mirror into the optical chain so that the beam was imaged onto the HRC detector through the WFC/HRC filter wheels. The SBC channel is selected by moving the fold mirror out of the beam to yield a two mirror optical chain that focuses light through the SBC filter wheel onto the SBC detector. The aberrated beam coronagraph was accessed by inserting a mechanism into the HRC optical chain. This mechanism positioned a substrate with two occulting spots at the aberrated telescope focal plane and an apodizer at the re-imaged exit pupil. While there is no mechanical reason why the coronagraph could not be used with the SBC, for health and safety reasons, use of the coronagraph is forbidden with the SBC.
Filter Wheels
ACS has three filter wheels: two shared by the WFC and HRC, and a separate wheel dedicated to the SBC. The WFC/HRC filter wheels contain the major filter sets. Each wheel also contains one clear WFC aperture and one clear HRC aperture (see Chapter 5 for more on filters). Before January 2007, parallel WFC and HRC observations were possible for some filter combinations (auto-parallels). Because the filter wheels were shared, it was not possible to independently select the filter for WFC and HRC parallel observations.
Calibration Lamp Systems
ACS has a calibration subsystem consisting of tungsten lamps and a deuterium lamp for internally flat-fielding each of the optical channels. The calibration lamps illuminate a diffuser on the rear surface of the ACS aperture door, which must be closed for calibration exposures. Under normal circumstances, users are not allowed to use the internal calibration lamps.
Post-Flash LED
An Opto Diode OD-800W light emitting diode (LED) is attached to the ACS/WFC instrument housing. It is used to post-flash the detector after an exposure has completed and the shutter has closed. The post-flash raises the background level of an image by illuminating the LED at a specified current level (LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH) and for a specified duration. Post-flash is typically employed to mitigate the effects of poor charge transfer efficiency (CTE), especially at low background levels, though its use is not recommended for most observations. For more details on the LED and post-flash calibration, see Sections 2.5 and 9.6, and ACS ISRs 2019-08, 2018-02, 2014-01, and 2006-07.
-
ACS Instrument Handbook
- • Acknowledgments
- • Change Log
- • Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Considerations and Changes After SM4
- Chapter 3: ACS Capabilities, Design and Operations
- Chapter 4: Detector Performance
- Chapter 5: Imaging
- Chapter 6: Polarimetry, Coronagraphy, Prism and Grism Spectroscopy
-
Chapter 7: Observing Techniques
- • 7.1 Designing an ACS Observing Proposal
- • 7.2 SBC Bright Object Protection
- • 7.3 Operating Modes
- • 7.4 Patterns and Dithering
- • 7.5 A Road Map for Optimizing Observations
- • 7.6 CCD Gain Selection
- • 7.7 ACS Apertures
- • 7.8 Specifying Orientation on the Sky
- • 7.9 Parallel Observations
- • 7.10 Pointing Stability for Moving Targets
- Chapter 8: Overheads and Orbit-Time Determination
- Chapter 9: Exposure-Time Calculations
-
Chapter 10: Imaging Reference Material
- • 10.1 Introduction
- • 10.2 Using the Information in this Chapter
-
10.3 Throughputs and Correction Tables
- • WFC F435W
- • WFC F475W
- • WFC F502N
- • WFC F550M
- • WFC F555W
- • WFC F606W
- • WFC F625W
- • WFC F658N
- • WFC F660N
- • WFC F775W
- • WFC F814W
- • WFC F850LP
- • WFC G800L
- • WFC CLEAR
- • HRC F220W
- • HRC F250W
- • HRC F330W
- • HRC F344N
- • HRC F435W
- • HRC F475W
- • HRC F502N
- • HRC F550M
- • HRC F555W
- • HRC F606W
- • HRC F625W
- • HRC F658N
- • HRC F660N
- • HRC F775W
- • HRC F814W
- • HRC F850LP
- • HRC F892N
- • HRC G800L
- • HRC PR200L
- • HRC CLEAR
- • SBC F115LP
- • SBC F122M
- • SBC F125LP
- • SBC F140LP
- • SBC F150LP
- • SBC F165LP
- • SBC PR110L
- • SBC PR130L
- • 10.4 Geometric Distortion in ACS
- • Glossary