3.2 Instrument Design
In this section, a high-level summary of the basic design of STIS is provided, concentrating on the information most relevant to HST observing proposals. Subsequent chapters provide more detailed information.
3.2.1 Detectors
STIS uses three large-format (1024 × 1024 pixel) detectors (see Chapter 7 for more details), as follows:
- A Scientific Image Technologies (SITe) CCD, called the
STIS/CCD, with ~0.05 arcsecond square pixels, covering a nominal 52 × 52 arcsecond square field of view (FOV), operating from 1640 to 10,300 Å. - A Cs2Te Multi-Anode Microchannel Array (MAMA) detector, called the
STIS/NUV-MAMA, with ~0.025 arcsecond square pixels, and a nominal 25 × 25 arcsecond square field of view (FOV), operating in the NUV from 1600 to 3100 Å. - A solar-blind CsI MAMA, the
STIS/FUV-MAMA, with ~0.025 arcsecond pixels, and a nominal 25 × 25 arcsecond square FOV, operating in the FUV from 1150 to 1700 Å.
The CCD
The CCD provides high quantum efficiency and good dynamic range in the NUV through NIR. The CCD produces a time-integrated image in the ACCUM data-taking mode. As with all CCDs, there is noise (read noise) and time (read time) associated with reading out the detector. Time-resolved work with this detector is done by taking a series of short exposures. The minimum exposure time is 0.1 second, and the minimum time between successive identical exposures is 45 seconds for full-frame, but can be reduced to 20 seconds for subarray readouts. CCD detectors are capable of high dynamic range observations. The dynamic range for a single exposure ultimately is limited by the depth of the CCD full well (144,000 electrons), which determines the total amount of charge (or counts) that can accumulate in any one pixel during any one exposure without causing saturation. For GAIN=1, it is further limited (to 33,000 electrons) by saturation in the gain amplifier. For more information about the CCD saturation, see Section 5.1.4 or STIS ISR 2015-06: CCD Saturation Effects. Cosmic rays will also affect all CCD exposures. CCD observations should be broken into multiple exposures (called CR-SPLITs) of no more than 1000 seconds each, whenever possible, to allow for the removal of cosmic rays in post-observation data processing; during Phase II you can specify the CR-SPLIT optional parameter to do this (see Chapter 11).
The MAMAs
The two MAMAs are photon-counting detectors which provide two-dimensional UV capability. They can be operated either in ACCUM mode, to produce a time-integrated image, or in TIME-TAG mode to produce an event stream with high (125 microseconds) time resolution. In ACCUM mode, photons are accumulated into a 2048 × 2048, 16-bit-per-element oversampled array. The data can be left in that over-sampled (or highres) format, which is the default for scientific exposures, or they can be binned to produce a 1024 × 1024 native-format image. Doppler correction for the spacecraft motion is applied automatically onboard for data taken in the higher spectral resolution ACCUM modes.
Because the STIS MAMA detectors can be damaged by high levels of illumination, their use is subject to both local (individual pixel) and global (total illumination on the detector) brightness limits. Due to the characteristics of the detectors and the associated electronics, the global count rate also exhibits a slight (but correctable) non-linearity. At very high global illumination rates (≥285,000 counts/s), however, the counting becomes incomplete in a way that is not correctable. At somewhat higher illumination rates, the MAMA detectors are subject to damage. We have therefore defined conservative absolute local and global count-rate limits, which translate to a set of configuration-dependent bright-object screening limits for observations with the STIS MAMA detectors. Sources which violate the absolute count-rate limits in a given configuration cannot be observed in that configuration, as discussed in Section 7.7; see also STIS ISRs 1996-28, 1996-31, and 1998-08. Note that additional screening limits have been adopted for M dwarfs, as this class of objects can exhibit large and unpredictable flares. Details regarding those screening limits and the procedure to follow for clearing observations of M dwarfs can be found in STIS ISR 2017-02.
Early concerns about the signal-to-noise attainable with the MAMAs have been alleviated by experience in orbit. Values of 50:1 per spectral resolution element in extracted spectra are routinely obtained for point sources with sufficient counting statistics when integrated over the extraction aperture. Higher signal-to-noise values of 100–300 can be obtained by stepping the target along the slit in the first-order modes, or by use of special multiple slits with the echelles (see Chapter 12). Current information indicates that the flat fields are stable to ±1–2%. See also Section 16.1.
Highres
The MAMA detectors have 1024 × 1024 physical or so-called native-format pixels. However, each count is detected by multiple electrodes, so the charge distribution among the electrodes can be used to centroid the incident charge cloud to subpixel resolution. The gain of the highres 2048 × 2048 mode is a ~10–30% increase in resolution at the price of the increased fixed-pattern noise due to poorly characterized charge partition among the electrodes. The highres flat fields have much more structure than the 1024 × 1024 flats, with adjacent columns and rows differing by ~30% in an off/on pattern whose variability is appreciably higher than for 1024 × 1024 format images. This effect and the inherently lower signal-to-noise ratio in the full resolution flat-field images (nominally ~20 to 1 per highres pixel) suggest that it may be difficult to routinely realize the benefit in resolution. However, we note that data taken in highres mode can always be binned to 1024 × 1024 on the ground in post-observation data processing, and since the extra overheads in highres mode are typically quite small, highres is the default data-taking mode for the MAMA. The pipeline bins the data to 1024 × 1024 format during calibration, so that the pipeline output calibrated images are native format (see the STIS Data Handbook for more details). We note, however, that a method of correcting the increased fixed-pattern noise in highres mode has been devised (see Jenkins & Tripp 2001, ApJS, 137, 297).
3.2.2 STIS Physical Configuration
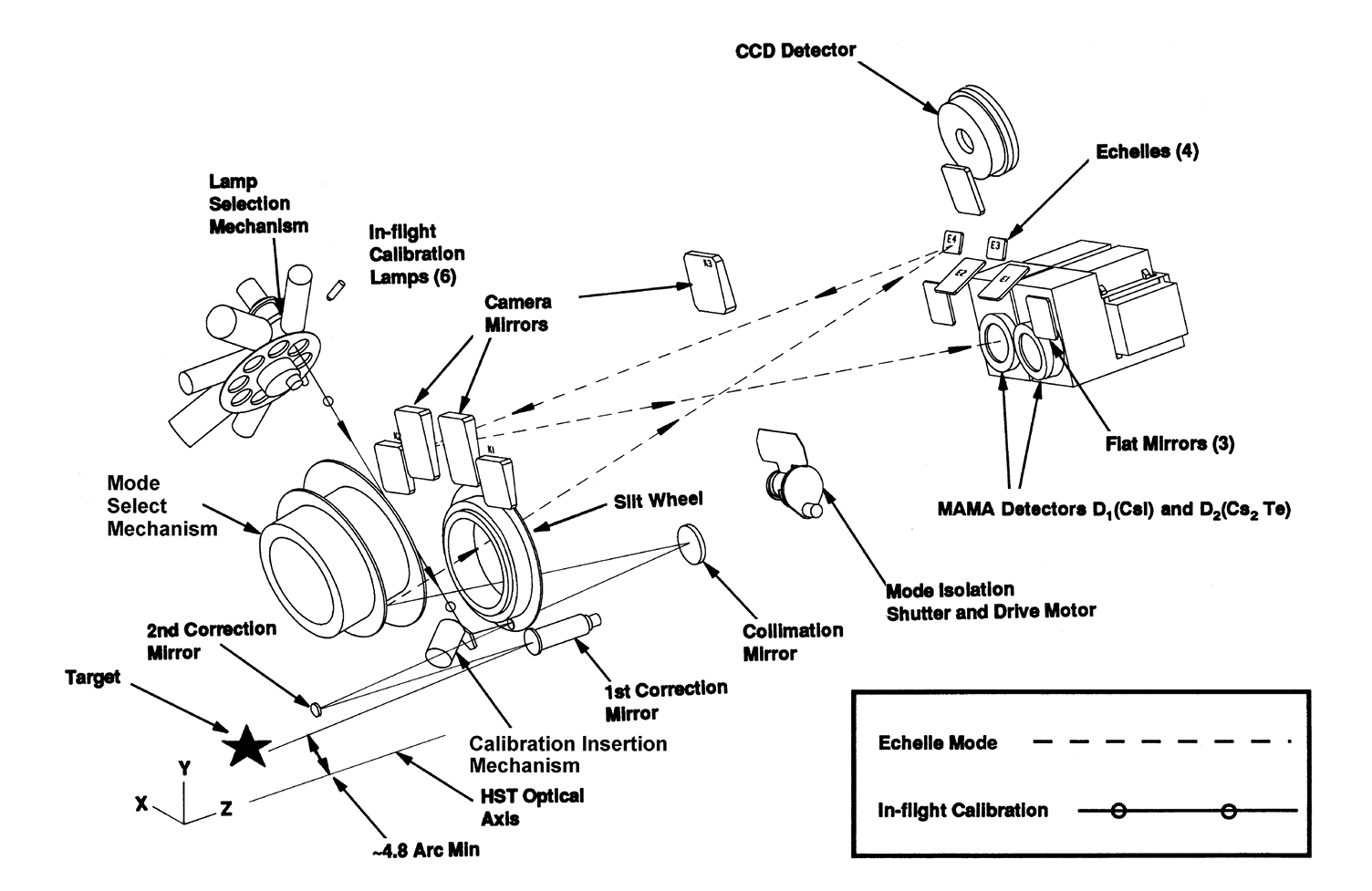
The STIS optical design includes corrective optics to compensate for HST's spherical aberration, a telescope focal plane slit-wheel assembly, collimating optics, a grating selection mechanism, fixed optics, and camera focal plane detectors. An independent calibration lamp assembly illuminates the focal plane with a range of continuum and emission line lamps. A simplified schematic showing major mechanisms and detectors, and a medium-resolution echelle mode light path is shown in Figure 3.1.
Slit and Grating Wheels
The slit wheel contains apertures and slits for spectroscopy and the clear, filtered, and coronagraphic apertures for imaging. Slit-wheel positioning is repeatable to very high precision: ±7.5 and ±2.5 milliarcseconds in the spatial and spectral directions, respectively.
The grating wheel, or so-called Mode Selection Mechanism (MSM), contains the first-order gratings, the cross-disperser gratings used with the echelles, the prism, and the mirrors used for imaging. The MSM is a nutating wheel which can orient optical elements in three dimensions. It permits the selection of one of its 21 optical elements as well as adjustment of the tip and tilt angles of the selected grating or mirror. As described in Routine Wavecals below, the grating wheel exhibits non-repeatability which is corrected for in post-observation data processing using contemporaneously obtained comparison-lamp exposures.
For some gratings, only a portion of the spectral range of the grating falls on the detector in any one exposure. These gratings can be scanned (tilted by the MSM) so that different segments of the spectral format are moved onto the detector for different exposures. For these gratings a set of pre-specified central wavelengths, corresponding to specific MSM positions, i.e., grating tilts, has been defined (see Chapter 4).
Calibration Lamp Systems
STIS has two independent calibration subsystems, the Hole in the Mirror (HITM) system and the Insert Mechanism (IM) system. The HITM system contains two Pt-Cr/Ne line lamps used to obtain wavelength calibration exposures and to illuminate the slit during target acquisitions. Light from the HITM lamps is projected through a hole in the second correction mirror (CM2). In some very early STIS data, the STIS external shutter was left open during the HITM wavecal exposure and the spectra of the lamp and the sky were recorded simultaneously. However, this is no longer an available option. Now the external shutter is always closed during the HITM lamp exposures. The IM system contains flat-fielding lamps (a tungsten lamp for CCD flats, a deuterium lamp for NUV-MAMA flats, and a krypton lamp for FUV-MAMA flats) and a single Pt-Cr/Ne line comparison lamp. When the IM lamps are used, the Calibration Insert Mechanism (CIM) is inserted into the light path and all external light is blocked. Observers will be relieved to know that the ground system will automatically choose the right subsystem (see Section 3.3) and provide the necessary wavelength calibration exposures.
-
STIS Instrument Handbook
- • Acknowledgments
- Chapter 1: Introduction
-
Chapter 2: Special Considerations for Cycle 33
- • 2.1 Impacts of Reduced Gyro Mode on Planning Observations
- • 2.2 STIS Performance Changes Pre- and Post-SM4
- • 2.3 New Capabilities for Cycle 33
- • 2.4 Use of Available-but-Unsupported Capabilities
- • 2.5 Choosing Between COS and STIS
- • 2.6 Scheduling Efficiency and Visit Orbit Limits
- • 2.7 MAMA Scheduling Policies
- • 2.8 Prime and Parallel Observing: MAMA Bright-Object Constraints
- • 2.9 STIS Snapshot Program Policies
- Chapter 3: STIS Capabilities, Design, Operations, and Observations
- Chapter 4: Spectroscopy
- Chapter 5: Imaging
- Chapter 6: Exposure Time Calculations
- Chapter 7: Feasibility and Detector Performance
-
Chapter 8: Target Acquisition
- • 8.1 Introduction
- • 8.2 STIS Onboard CCD Target Acquisitions - ACQ
- • 8.3 Onboard Target Acquisition Peakups - ACQ PEAK
- • 8.4 Determining Coordinates in the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) Reference Frame
- • 8.5 Acquisition Examples
- • 8.6 STIS Post-Observation Target Acquisition Analysis
- Chapter 9: Overheads and Orbit-Time Determination
- Chapter 10: Summary and Checklist
- Chapter 11: Data Taking
-
Chapter 12: Special Uses of STIS
- • 12.1 Slitless First-Order Spectroscopy
- • 12.2 Long-Slit Echelle Spectroscopy
- • 12.3 Time-Resolved Observations
- • 12.4 Observing Too-Bright Objects with STIS
- • 12.5 High Signal-to-Noise Ratio Observations
- • 12.6 Improving the Sampling of the Line Spread Function
- • 12.7 Considerations for Observing Planetary Targets
- • 12.8 Special Considerations for Extended Targets
- • 12.9 Parallel Observing with STIS
- • 12.10 Coronagraphic Spectroscopy
- • 12.11 Coronagraphic Imaging - 50CORON
- • 12.12 Spatial Scans with the STIS CCD
-
Chapter 13: Spectroscopic Reference Material
- • 13.1 Introduction
- • 13.2 Using the Information in this Chapter
-
13.3 Gratings
- • First-Order Grating G750L
- • First-Order Grating G750M
- • First-Order Grating G430L
- • First-Order Grating G430M
- • First-Order Grating G230LB
- • Comparison of G230LB and G230L
- • First-Order Grating G230MB
- • Comparison of G230MB and G230M
- • First-Order Grating G230L
- • First-Order Grating G230M
- • First-Order Grating G140L
- • First-Order Grating G140M
- • Echelle Grating E230M
- • Echelle Grating E230H
- • Echelle Grating E140M
- • Echelle Grating E140H
- • PRISM
- • PRISM Wavelength Relationship
-
13.4 Apertures
- • 52X0.05 Aperture
- • 52X0.05E1 and 52X0.05D1 Pseudo-Apertures
- • 52X0.1 Aperture
- • 52X0.1E1 and 52X0.1D1 Pseudo-Apertures
- • 52X0.2 Aperture
- • 52X0.2E1, 52X0.2E2, and 52X0.2D1 Pseudo-Apertures
- • 52X0.5 Aperture
- • 52X0.5E1, 52X0.5E2, and 52X0.5D1 Pseudo-Apertures
- • 52X2 Aperture
- • 52X2E1, 52X2E2, and 52X2D1 Pseudo-Apertures
- • 52X0.2F1 Aperture
- • 0.2X0.06 Aperture
- • 0.2X0.2 Aperture
- • 0.2X0.09 Aperture
- • 6X0.2 Aperture
- • 0.1X0.03 Aperture
- • FP-SPLIT Slits 0.2X0.06FP(A-E) Apertures
- • FP-SPLIT Slits 0.2X0.2FP(A-E) Apertures
- • 31X0.05ND(A-C) Apertures
- • 0.2X0.05ND Aperture
- • 0.3X0.05ND Aperture
- • F25NDQ Aperture
- 13.5 Spatial Profiles
- 13.6 Line Spread Functions
- • 13.7 Spectral Purity, Order Confusion, and Peculiarities
- • 13.8 MAMA Spectroscopic Bright Object Limits
-
Chapter 14: Imaging Reference Material
- • 14.1 Introduction
- • 14.2 Using the Information in this Chapter
- 14.3 CCD
- 14.4 NUV-MAMA
-
14.5 FUV-MAMA
- • 25MAMA - FUV-MAMA, Clear
- • 25MAMAD1 - FUV-MAMA Pseudo-Aperture
- • F25ND3 - FUV-MAMA
- • F25ND5 - FUV-MAMA
- • F25NDQ - FUV-MAMA
- • F25QTZ - FUV-MAMA, Longpass
- • F25QTZD1 - FUV-MAMA, Longpass Pseudo-Aperture
- • F25SRF2 - FUV-MAMA, Longpass
- • F25SRF2D1 - FUV-MAMA, Longpass Pseudo-Aperture
- • F25LYA - FUV-MAMA, Lyman-alpha
- • 14.6 Image Mode Geometric Distortion
- • 14.7 Spatial Dependence of the STIS PSF
- • 14.8 MAMA Imaging Bright Object Limits
- Chapter 15: Overview of Pipeline Calibration
- Chapter 16: Accuracies
-
Chapter 17: Calibration Status and Plans
- • 17.1 Introduction
- • 17.2 Ground Testing and Calibration
- • 17.3 STIS Installation and Verification (SMOV2)
- • 17.4 Cycle 7 Calibration
- • 17.5 Cycle 8 Calibration
- • 17.6 Cycle 9 Calibration
- • 17.7 Cycle 10 Calibration
- • 17.8 Cycle 11 Calibration
- • 17.9 Cycle 12 Calibration
- • 17.10 SM4 and SMOV4 Calibration
- • 17.11 Cycle 17 Calibration Plan
- • 17.12 Cycle 18 Calibration Plan
- • 17.13 Cycle 19 Calibration Plan
- • 17.14 Cycle 20 Calibration Plan
- • 17.15 Cycle 21 Calibration Plan
- • 17.16 Cycle 22 Calibration Plan
- • 17.17 Cycle 23 Calibration Plan
- • 17.18 Cycle 24 Calibration Plan
- • 17.19 Cycle 25 Calibration Plan
- • 17.20 Cycle 26 Calibration Plan
- • 17.21 Cycle 27 Calibration Plan
- • 17.22 Cycle 28 Calibration Plan
- • 17.23 Cycle 29 Calibration Plan
- • 17.24 Cycle 30 Calibration Plan
- • 17.25 Cycle 31 Calibration Plan
- • 17.26 Cycle 32 Calibration Plan
- Appendix A: Available-But-Unsupported Spectroscopic Capabilities
- • Glossary