4.3 Echelle Spectroscopy in the Ultraviolet
An example of STIS E230H echelle spectroscopy (both the echelle spectrum and a few sample extracted orders) of star CPD-59D2603 showing the interstellar absorption from the Carina Nebula is given in Figure 15.3. (See also Walborn et al. 1998, ApJ, 492, L169.)
4.3.1 Echelle Gratings
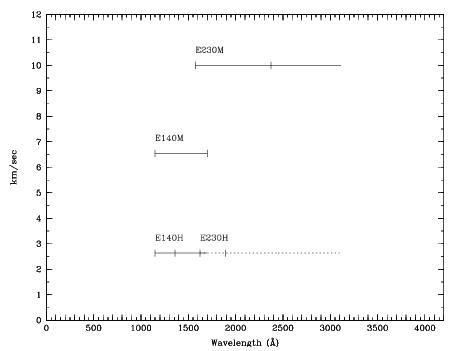
There are four echelle grating modes that provide spectroscopic coverage from ~1145 Å to 3100 Å at resolving powers from R ~ 30,000 to R ~ 114,000 (or even R ~ 200,000 with the 0.1X0.03 aperture and specialized data reduction; see Section 12.6). Through simultaneous observation of multiple orders, they are designed to maximize the spectral coverage achieved in a single exposure of a point source. Figure 4.10 below summarizes the wavelength coverage and kinematic resolutions of the echelle gratings. In short:
- For ~10 km/s resolution use:
E140Mat 1144–1730 Å.E230Mat 1600–3100 Å.
- For ~2.5 km/s resolution use:
E140Hat 1140–1700 Å.E230Hat 1600–3100 Å.
E230H coverage. See Table 4.1 and Chapter 13 for more details.4.3.2 Slits for Echelle Spectroscopy
Short echelle slits, which ensure order separation, are available for use with the echelle gratings. For each mode a short slit of width 0.2 arcsecond is provided, along with a slit whose width matches a two pixel projection in the dispersion direction; either 0.09 arcsecond for the H modes, or 0.06 arcsecond for the M modes. In addition, an ultra-narrow slit of width 0.025 arcsecond (0.1X0.03 in the Proposal Instructions) is supported with all of the echelles, for the highest spectral resolution of bright objects. Also, two multi-slits with different widths (called the FP-SPLIT slits) are supported for use with the echelles to provide optimally placed multiple exposures which maximize S/N. Their use is discussed in Chapter 12.
Although we do not recommend routine use, the echelle gratings can be used with a long slit (the 6X0.2 slit) to obtain echelle spectroscopy of extended objects with weak continua. Long-slit echelle data, however, will not be calibrated by the STScI pipeline, and they will require more extensive post-observation processing by the user since ambiguous overlap of wavelengths from different parts of sources will occur in the image (see Section 12.2 if you are considering such observations). In addition to the spectral purity considerations in the dispersion direction mentioned above for the first-order gratings, echelle observations are subject to contamination in the cross-dispersion direction by scattered light. This effect is aggravated toward shorter wavelengths as the orders become more crowded. Continuum sources should not normally be observed with slit lengths greater than 0.2 arcsecond, and even then special data analysis may be required to optimize the accuracy of the results. See Section 13.7.
4.3.3 Detailed Echelle Information
The properties of each of the echelle gratings are described in detail, grating by grating, in Chapter 13; see the first column of Table 4.1 for links to the appropriate page for each grating.
The detailed properties of the echelle slits (e.g., throughputs and line spreads as functions of wavelength), the plate scales, and the encircled energies for the echelle modes are presented under Section 13.4, Section 13.5, and Section 13.6.
-
STIS Instrument Handbook
- • Acknowledgments
- Chapter 1: Introduction
-
Chapter 2: Special Considerations for Cycle 33
- • 2.1 Impacts of Reduced Gyro Mode on Planning Observations
- • 2.2 STIS Performance Changes Pre- and Post-SM4
- • 2.3 New Capabilities for Cycle 33
- • 2.4 Use of Available-but-Unsupported Capabilities
- • 2.5 Choosing Between COS and STIS
- • 2.6 Scheduling Efficiency and Visit Orbit Limits
- • 2.7 MAMA Scheduling Policies
- • 2.8 Prime and Parallel Observing: MAMA Bright-Object Constraints
- • 2.9 STIS Snapshot Program Policies
- Chapter 3: STIS Capabilities, Design, Operations, and Observations
- Chapter 4: Spectroscopy
- Chapter 5: Imaging
- Chapter 6: Exposure Time Calculations
- Chapter 7: Feasibility and Detector Performance
-
Chapter 8: Target Acquisition
- • 8.1 Introduction
- • 8.2 STIS Onboard CCD Target Acquisitions - ACQ
- • 8.3 Onboard Target Acquisition Peakups - ACQ PEAK
- • 8.4 Determining Coordinates in the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) Reference Frame
- • 8.5 Acquisition Examples
- • 8.6 STIS Post-Observation Target Acquisition Analysis
- Chapter 9: Overheads and Orbit-Time Determination
- Chapter 10: Summary and Checklist
- Chapter 11: Data Taking
-
Chapter 12: Special Uses of STIS
- • 12.1 Slitless First-Order Spectroscopy
- • 12.2 Long-Slit Echelle Spectroscopy
- • 12.3 Time-Resolved Observations
- • 12.4 Observing Too-Bright Objects with STIS
- • 12.5 High Signal-to-Noise Ratio Observations
- • 12.6 Improving the Sampling of the Line Spread Function
- • 12.7 Considerations for Observing Planetary Targets
- • 12.8 Special Considerations for Extended Targets
- • 12.9 Parallel Observing with STIS
- • 12.10 Coronagraphic Spectroscopy
- • 12.11 Coronagraphic Imaging - 50CORON
- • 12.12 Spatial Scans with the STIS CCD
-
Chapter 13: Spectroscopic Reference Material
- • 13.1 Introduction
- • 13.2 Using the Information in this Chapter
-
13.3 Gratings
- • First-Order Grating G750L
- • First-Order Grating G750M
- • First-Order Grating G430L
- • First-Order Grating G430M
- • First-Order Grating G230LB
- • Comparison of G230LB and G230L
- • First-Order Grating G230MB
- • Comparison of G230MB and G230M
- • First-Order Grating G230L
- • First-Order Grating G230M
- • First-Order Grating G140L
- • First-Order Grating G140M
- • Echelle Grating E230M
- • Echelle Grating E230H
- • Echelle Grating E140M
- • Echelle Grating E140H
- • PRISM
- • PRISM Wavelength Relationship
-
13.4 Apertures
- • 52X0.05 Aperture
- • 52X0.05E1 and 52X0.05D1 Pseudo-Apertures
- • 52X0.1 Aperture
- • 52X0.1E1 and 52X0.1D1 Pseudo-Apertures
- • 52X0.2 Aperture
- • 52X0.2E1, 52X0.2E2, and 52X0.2D1 Pseudo-Apertures
- • 52X0.5 Aperture
- • 52X0.5E1, 52X0.5E2, and 52X0.5D1 Pseudo-Apertures
- • 52X2 Aperture
- • 52X2E1, 52X2E2, and 52X2D1 Pseudo-Apertures
- • 52X0.2F1 Aperture
- • 0.2X0.06 Aperture
- • 0.2X0.2 Aperture
- • 0.2X0.09 Aperture
- • 6X0.2 Aperture
- • 0.1X0.03 Aperture
- • FP-SPLIT Slits 0.2X0.06FP(A-E) Apertures
- • FP-SPLIT Slits 0.2X0.2FP(A-E) Apertures
- • 31X0.05ND(A-C) Apertures
- • 0.2X0.05ND Aperture
- • 0.3X0.05ND Aperture
- • F25NDQ Aperture
- 13.5 Spatial Profiles
- 13.6 Line Spread Functions
- • 13.7 Spectral Purity, Order Confusion, and Peculiarities
- • 13.8 MAMA Spectroscopic Bright Object Limits
-
Chapter 14: Imaging Reference Material
- • 14.1 Introduction
- • 14.2 Using the Information in this Chapter
- 14.3 CCD
- 14.4 NUV-MAMA
-
14.5 FUV-MAMA
- • 25MAMA - FUV-MAMA, Clear
- • 25MAMAD1 - FUV-MAMA Pseudo-Aperture
- • F25ND3 - FUV-MAMA
- • F25ND5 - FUV-MAMA
- • F25NDQ - FUV-MAMA
- • F25QTZ - FUV-MAMA, Longpass
- • F25QTZD1 - FUV-MAMA, Longpass Pseudo-Aperture
- • F25SRF2 - FUV-MAMA, Longpass
- • F25SRF2D1 - FUV-MAMA, Longpass Pseudo-Aperture
- • F25LYA - FUV-MAMA, Lyman-alpha
- • 14.6 Image Mode Geometric Distortion
- • 14.7 Spatial Dependence of the STIS PSF
- • 14.8 MAMA Imaging Bright Object Limits
- Chapter 15: Overview of Pipeline Calibration
- Chapter 16: Accuracies
-
Chapter 17: Calibration Status and Plans
- • 17.1 Introduction
- • 17.2 Ground Testing and Calibration
- • 17.3 STIS Installation and Verification (SMOV2)
- • 17.4 Cycle 7 Calibration
- • 17.5 Cycle 8 Calibration
- • 17.6 Cycle 9 Calibration
- • 17.7 Cycle 10 Calibration
- • 17.8 Cycle 11 Calibration
- • 17.9 Cycle 12 Calibration
- • 17.10 SM4 and SMOV4 Calibration
- • 17.11 Cycle 17 Calibration Plan
- • 17.12 Cycle 18 Calibration Plan
- • 17.13 Cycle 19 Calibration Plan
- • 17.14 Cycle 20 Calibration Plan
- • 17.15 Cycle 21 Calibration Plan
- • 17.16 Cycle 22 Calibration Plan
- • 17.17 Cycle 23 Calibration Plan
- • 17.18 Cycle 24 Calibration Plan
- • 17.19 Cycle 25 Calibration Plan
- • 17.20 Cycle 26 Calibration Plan
- • 17.21 Cycle 27 Calibration Plan
- • 17.22 Cycle 28 Calibration Plan
- • 17.23 Cycle 29 Calibration Plan
- • 17.24 Cycle 30 Calibration Plan
- • 17.25 Cycle 31 Calibration Plan
- • 17.26 Cycle 32 Calibration Plan
- Appendix A: Available-But-Unsupported Spectroscopic Capabilities
- • Glossary